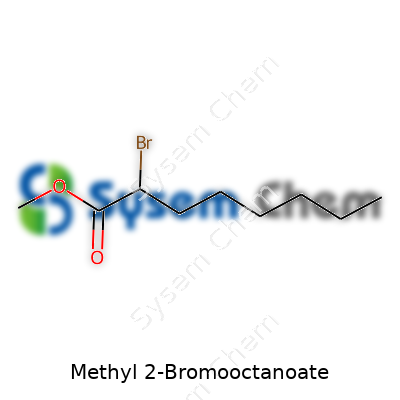
Methyl 2-Bromooctanoate: A Practical Commentary
Historical Development
Scientists have known about Methyl 2-Bromooctanoate for several decades, and its development tracks closely with the expansion of organic bromine chemistry in the twentieth century. In my experience, brominated esters like this one emerged as key intermediates during the period when pharmaceutical synthesis and industrial surfactant production demanded more selective and reactive pathways. Methyl 2-Bromooctanoate carved out its own niche by bridging gaps in both academic laboratories and large-scale manufacturing, mainly due to its flexibility as a building block and its readiness to undergo further chemical transformation. Early methods leaned on labor-intensive processes, but step by step, researchers tweaked reaction conditions, solvent systems, and workup steps to handle the compound more safely and efficiently. The importance of this compound only grew as chemists dove deeper into complex molecule construction.
Product Overview
Methyl 2-Bromooctanoate doesn’t turn heads like some advanced pharmaceutical compounds, but for chemists who wrestle with synthetic challenges, its value comes across in versatility. This clear to pale yellow liquid serves as a simple, reliable intermediate. It offers a point of entry for more complex molecules, especially where an eight-carbon chain and a reactive bromine handle matter. Manufacturers ship it in airtight containers, well aware that the product’s quality and purity can make or break a downstream reaction. Academic researchers and industry process chemists share one thing here – reliability stands above all.
Physical & Chemical Properties
Anyone who opens a flask of Methyl 2-Bromooctanoate notices a sharp, sometimes sweet odor, a sign that the molecule carries moderate volatility. Its boiling point hovers around 110-114°C at low pressure, with a density just above that of water. This compound definitely suits environments where both non-polar and polar solvents play a role. Its ester group makes it susceptible to hydrolysis, while the bromine atom at the secondary carbon opens up all sorts of substitution and elimination pathways. Solubility trends set it apart from heavier, stickier brominated oils. Clear separation from water and good miscibility with organic solvents streamline reaction planning.
Technical Specifications & Labeling
Technical-grade Methyl 2-Bromooctanoate doesn’t cut corners on purity. I’ve spent too many hours troubleshooting reactions only to find out impurities trace back to poorly specified compounds. Reputable suppliers label bottles with GC assay data, usually topping 98%. Alongside this, material safety data sheets share boiling and flash points, storage advice, and hazard codes. Unambiguous labeling really saves time for everyone in the lab or pilot plant. Mishandling or incorrect identification only sets projects back. Documentation must keep up with global trade, so IUPAC names, CAS numbers, and traditional synonyms go right on the label to avoid confusion between different regional suppliers.
Preparation Method
Laboratory prep typically begins with octanoic acid, moving through esterification to yield methyl octanoate, and finishing with bromination at the alpha position. Most protocols rely on a halogenation agent like N-bromosuccinimide, keeping a careful watch on temperature and reaction times to prevent unwanted dibromination. This stepwise approach still dominates because it balances straightforward chemistry with manageable waste streams. Industry leans on optimized flow systems to boost throughput and reduce exposure to hazardous bromine reagents. One thing stands out: carrying out this sequence demands steady hands and respect for temperature control.
Chemical Reactions & Modifications
Methyl 2-Bromooctanoate plays nicely with a range of nucleophiles. Swap out bromine with amines, alkoxides, or even simple cyanide, and new molecules sprout from the backbone, all thanks to the accessible alpha-position. Chemists leverage these reactions to stitch together longer chains, build more branched molecules, or install functional groups critical for biological activity. I recall one route to a beta-amino acid that relied entirely on clean displacement of the bromine. The ester group holds steady under many reaction conditions, suiting sequences that run through several stages. Reduction, hydrolysis, and transesterification all fall within reach, letting teams shuffle structures to meet whatever challenge comes next.
Synonyms & Product Names
Chemistry circles use a handful of synonyms for this compound, each one reflecting its molecular structure. Names like "Methyl 2-bromo-caprylate", "2-Bromooctanoic acid methyl ester," and simply "BMO" appear in catalogs and research journals. Keeping track matters because even a slight misreading can send a researcher after the wrong material. Strict adherence to IUPAC conventions might sound tedious, but pharmaceutical and regulatory teams appreciate the clarity. Labeling errors slow down projects and create paperwork headaches that overshadow simple tasks.
Safety & Operational Standards
Brominated compounds like Methyl 2-Bromooctanoate deserve healthy respect. Vapors tend to irritate eyes, nose, and skin, and accidental spills make for headaches in both academic and industrial settings. Fume hoods, gloves, and goggles head the list of must-have gear here. Teams using large volumes depend on proper ventilation and rigorous waste disposal plans. I’ve seen labs save trouble by installing dedicated quench and neutralization tanks, keeping the bromine out of shared drains. Safety data emphasize proper storage – keeping bottles away from oxidizers, open flames, and moisture. Following these standards reduces downtime caused by workplace accidents, and gets teams back on track faster.
Application Area
Drug discovery efforts put Methyl 2-Bromooctanoate front and center as a starting material and as a reactive intermediate. Peptide mimics, beta-amino acids, and several antiviral agents trace their origins back to clever use of this compound. Where surfactants require specialized chain lengths, custom brominated esters open up performance tweaks unavailable with shorter or longer chains. More than once, I’ve watched process engineers switch to Methyl 2-Bromooctanoate just to shortcut a bottleneck in traditional fatty acid modification. Agricultural chemical development borrows it too, tailoring molecules for better uptake or slower degradation in soil. The scale (from grams to tons) shows just how far this simple molecule reaches across product lines.
Research & Development
Every year, research teams publish tweaks and modifications to the classic synthesis routes. Fresh catalytic systems crop up, promising cleaner yields or fewer steps. In my own work, I’ve noticed that every improvement – whether it’s a solvent swap or a drop-in new brominating agent – continues to push the molecule’s reach further. Biocatalysis and flow chemistry both show promise, letting labs cut solvent waste and bump up yields. Some groups tinker with enantioselective bromination, hunting for ways to turn out only one mirror image of the product, which matters enormously for drug work. Journals fill with ideas, but only those backed up by scalable results find a foothold in commercial production.
Toxicity Research
The safety of Methyl 2-Bromooctanoate falls under close watch because both esters and brominated organics often stir concern. Early toxicity screens placed it in the caution zone for skin and respiratory irritation. Animal studies shed light on its metabolic fate – hydrolysis and debromination step in quickly once it hits biological systems. Regulatory boards keep a close eye on workplace exposure and end-product residues, pushing companies to invest in both detection methods and mitigation steps. I’ve seen protocols shift to closed systems or single-use gloves after just one incident of contact dermatitis. Long-term data stays thin, but continued monitoring matters as use spreads into new industries.
Future Prospects
Sustainable chemistry gets more attention every year, so Methyl 2-Bromooctanoate stands at a crossroads. Green bromination techniques, biocatalytic modifications, and safer downstream processing beckon the industry forward. Researchers experiment with bio-based octanoic acid sources, making the pathway less reliant on fossil feedstocks. Industrial teams pilot continuous-flow reactors to shrink energy use and waste generation. New application areas keep cropping up, from specialty lubricants to advanced materials. Those who stay on top of greener, safer technology will shape where this versatile molecule fits in the next decade. Commitment to safety, robust process validation, and agile R&D point toward a future with fewer hazards and even broader impact.
The Formula: C9H17BrO2
In labs and classrooms, methyl 2-bromooctanoate carries a formula: C9H17BrO2. These numbers and letters line up to describe a molecule with nine carbons, seventeen hydrogens, a bromine, and two oxygens. It lands in textbooks and lectures as part of the story behind how chemists build bigger ideas from simple building blocks.
Why This Compound Draws Attention
Methyl 2-bromooctanoate stands out to organic chemists for a reason. The long carbon chain and the bromine atom make it a handy piece in synthesis. Manipulating this molecule helps researchers craft customized compounds—anything from pharmaceuticals to specialty plastics. In my own experience working with esters, having a functional handle like bromine opens up routes you just can't take with plainer molecules. Want to swap that bromine for something else? The options explode, opening pathways to molecules that show up in real-world products.
Chemical Properties and Real Uses
It acts as an alpha-bromo ester, so it reacts in ways that can seem almost predictable. Chemists rely on it for preparing more complex molecules, including drugs and lab reagents with very specific purposes. I remember using a similar starting material to build a series of intermediates that our team tweaked for medicinal research. Once you have a halogen on the chain, you almost feel like you've unlocked a cheat code. That little twist in the structure supports alkylation, nucleophilic substitution, and other common reactions.
Safe Handling: Facts and Experience
Lab safety isn’t a nice-to-have; it comes from the reality that all chemicals need respect. For methyl 2-bromooctanoate, gloves and goggles aren’t optional. Bromine-containing compounds often present hazards—skin and eye irritation, and sometimes more severe health risks if inhaled or ingested. Good ventilation and well-labeled storage mark the line between smart work and unnecessary accidents. In the lab, I've seen careless handling turn an easy day into hours filling out incident reports.
Addressing Environmental and Ethical Challenges
Scaling up chemical synthesis brings real-world concerns. Where do all those bromo-derivatives and solvent residues go? Down-the-drain chemistry no longer fits with environmental responsibility. Collaborating with colleagues, I’ve learned the value of simple practices—waste segregation, diligent labeling, commitment to green chemistry principles. Embracing these habits becomes more than a box-ticking exercise; it’s about protecting the planet and the people who come after us.
Finding Solutions That Balance Progress and Responsibility
Some labs push for alternative reagents and processes that generate less hazardous waste. Researchers scrutinize reaction steps to cut down on harmful byproducts and swap out toxic solvents. These improvements matter most in places where waste management choices shape community health. The call for more sustainable chemistry comes from both inside and outside the lab. People deserve transparency in how these chemicals get made, used, and disposed.
Moving Forward
The formula C9H17BrO2 unlocks possibilities, but responsibility sits in every beaker. Commitment to safety and sustainability stands as the foundation of modern chemistry. Awareness and ongoing learning keep this science grounded in ethics as much as in equations.
Digging into the Basics
People who spend time in a synthetic chemistry lab know molecules like Methyl 2-Bromooctanoate bring a certain level of excitement. This compound, built with a bromine atom on an eight-carbon fatty acid chain, doesn’t make headlines. Yet, it quietly holds importance in different areas of research and production. Its value tends to shine in hands that use it to shape something bigger—whether in pharmaceuticals, the agrochemical sector, or advanced materials.
Fuel for Medicine and Research
Pharmaceutical research feeds off chemicals that can react in controlled, selective ways. Methyl 2-Bromooctanoate offers this by acting as a building block for more complex molecules. Chemists use it to add specific chains or to attach functional groups they need. In my experience talking to medicinal chemists, they often look for molecules that let them tinker with drug candidates' structures easily. With Methyl 2-Bromooctanoate, the bromine makes it easy to swap out atoms and adjust molecular shapes. That helps researchers seek out new antibiotics, antivirals, or compounds with other medical potential.
This compound provides a shortcut in multi-step syntheses. One chemist once explained the savings in time—taking a couple of days off long synthetic routes. Time matters, and when you work with hundreds of compounds, even small efficiencies can be a big deal.
Plant Protection and Chemical Innovation
On the agricultural side, Methyl 2-Bromooctanoate steps in as a useful ingredient for synthesizing various crop protection agents. Farmers rely on products that shield crops from insects or fungi, and chemical producers use this molecule to help create new classes of pesticides or herbicides. According to published industry reports, companies looking for eco-friendlier chemicals favor starting materials like this ester for their versatility and manageable reactivity.
The reason? The octanoate chain brings both lipid solubility and chemical stability, which supports products that need to last outdoors on plants—or break down safely after use. Regulatory agencies examine these safety profiles closely, and small tweaks at the molecular level can tip the balance toward approval.
Material Science and Specialty Applications
Another place Methyl 2-Bromooctanoate turns up is in materials research. Scientists interested in new coatings, lubricants, or surfactants start with molecules like this. In a past project focused on polymer design, we looked for intermediates that would add flexibility and water-resistance to finished materials. Compounds like Methyl 2-Bromooctanoate, with long fatty chains, fit the bill and blend well with other ingredients.
In electronics, its derivatives play a role in synthesizing specialty polymers or as part of the manufacturing process for liquid crystals—those same materials powering display screens. Every small advantage—higher purity, more controlled structure—counts here, since small impurities can knock sensitive devices off track.
Looking Forward: Addressing Safety and Sustainability
Widespread use of molecules like this always brings up safety and environmental questions. Researchers and manufacturers focus on limiting exposure, containing waste, and finding green chemistry solutions. Some teams are running projects on recycling brominated byproducts or using renewable feedstocks to produce methyl esters.
With growing demand for sustainable manufacturing, every link in the supply chain gets examined. Academic groups share data on improved synthesis routes that cut hazardous waste. Industry partners join in, sharing risk assessments and supporting safer protocols.
Final Thoughts on Utility and Impact
Methyl 2-Bromooctanoate rarely lands in consumer products directly, but it makes an essential stop on the path toward new medicines, safer crop protectants, and higher-performance materials. Each field pushes the limits of what’s possible, and this chemical gives them room to innovate without starting from zero. For anyone tracking what’s next in chemical applications, keeping an eye on how and where compounds like this show up uncovers a lot about broader trends in science and manufacturing.
Why Proper Storage Matters
Methyl 2-Bromooctanoate doesn’t usually get much spotlight outside chemistry circles, but anyone who has handled it in a lab knows mistakes here can bring headaches fast. This organobromide, useful for making complex molecules, won’t announce its own needs—so safe, stable storage is all about how we pay attention. Losing a batch to contamination or decomposition gets expensive, risky, and disrupts project timelines. I’ve seen labs skip basics and lose not just product, but safety, which nobody forgets in a hurry.
Temperature and Light Control
Temperature holds a seat at the table for chemical longevity. Once, storing sensitive compounds near a sunlit window led to visible discoloration in a matter of days. Methyl 2-Bromooctanoate fares better on a cool shelf, away from sunlight. Aim for room temperature, but a touch cooler—some teams reach for around 2–8°C if the supply will sit for a long time. Don’t freeze it, though. Sudden temp swings invite condensation and mess with the cap’s tightness. Humidity creeps in quietly and spoils reactivity faster than you expect.
Keep Out Moisture and Air
Anyone who’s uncapped a bottle only to catch a whiff knows water and air turn reactive organics into trouble. Moisture, even from the air, attacks that ester bond and breaks it down. I learned early to keep desiccant packs handy and check them regularly—too many times, folks throw in a pack once and never swap it out, which does no good. Every time a bottle opens, oxygen sneaks in, providing a path for oxidation changes that nobody wants. Sealing the container tightly after every use slows the decay and keeps the chemistry predictable.
Pick the Right Containers
Glass stands up to methyl 2-bromooctanoate’s personality better than most plastics. Some plastics absorb or react with organobromides, leading to lost product and a sticky, confusing mess inside the container. Amber glass works best, blocking out harsh light. At my previous workplace, a switch from clear to amber bottles cut our loss rate by a third, just from less light exposure. If you label your bottle clearly, fellow chemists won’t waste time deciphering faded ink or guessing at contents. Avoid using makeshift lids—original caps fit snug and prevent vapor loss.
Smart Handling Reduces Accidents
Always prep before you touch the chemical. Gloves, goggles, and a well-ventilated space reduce risk. Spills clean up easier on metal or chemical-resistant worktops, not wood or paper. One time, a colleague poured a small amount back into the stock bottle; by month’s end, the whole supply turned yellow. Contaminated transfers create problems that show up later, often right in the middle of a reaction. Use clean tools, dedicate spatulas, and never pipette by mouth (I still hear older chemists joke about the “good old days”—nobody misses them).
Why Good Practice Matters for Everyone
Methyl 2-Bromooctanoate isn’t unique in its needs, but every chemist who treats storage lightly increases the risk for the whole lab. Nobody wants mystery side products showing up because a bottle sat too warm, loose, or wet. Safety goes beyond compliance checkmarks. Keeping this compound stable means fewer wasted experiments, less time rewinding procedures, and more peace of mind at the bench. Bring your own common sense and learn from every slip—future you (and your colleagues) will appreciate the extra care.
Understanding What Methyl 2-Bromooctanoate Is
Methyl 2-bromooctanoate has a name that feels like a chemistry pop quiz. The compound belongs to a group of chemicals known as alkyl bromides, showing up in research labs and sometimes in chemical companies’ catalogs. For people not used to handling chemicals, any substance with “bromo” or “octanoate” in its name can ring alarm bells, and for good reason. Many organic bromides have a track record of causing harm, especially if someone accidentally inhales fumes or lets them touch bare skin.
Evidence on Hazards and Toxicity
Diving into safety data sheets and toxicology reports, most methyl 2-bromooctanoate information comes from laboratory settings. The main risk comes from its reactivity and its ability to irritate. We’re not talking about cyanide-level danger, but exposure raises fair concerns. It can irritate eyes, skin, and mucous membranes. Several brominated compounds are known for toxicity concerns—including some that disrupt hormones in living things.
Data on long-term effects is slim, which can be more troubling than a clear red flag. Most compounds in this category aren’t given the benefit of the doubt when safe handling is on the line. Lab professionals treat even tiny amounts with gloves and fume hoods. Accidental splashes, spills, or breathing in vapors should mean a visit to the eyewash station or a call to the local hazardous materials office.
Why Risk Assessment Matters
Companies that make or use substances like methyl 2-bromooctanoate carry a responsibility to protect their workers. Just because something isn’t famous for causing disaster doesn’t mean it’s harmless. Regular people don’t encounter it at home, but anyone at a research bench learns quickly to respect chemicals they can’t easily pronounce.
I remember being a graduate student in a chemistry lab, where the whole attitude was “assume the worst, take every precaution.” No shortcut is worth a chemical burn or a trip to the emergency room. There’s comfort in knowing best lab practices come straight from hard lessons learned by those who went before. Try holding a cracked pipette full of a brominated ester just once and see how quickly you look for a better way next time.
Supporting Safety with Real Tools and Training
The EPA, OSHA, and other agencies offer fact sheets and guidance for working with chemicals like methyl 2-bromooctanoate. Wearing gloves, goggles, and working with proper ventilation go further than any guesswork. Good record-keeping also helps: accidents can happen, but accurate info about what was on hand can make the difference in an emergency.
Disposal is another issue that can’t be ignored. Flushing brominated compounds down the drain or tossing them in the trash leads to trouble for local water supplies and garbage workers. Chemical waste contracts and strict labeling protect more people than just chemists.
Moving Forward: Attention and Transparency
Factories and universities support a safety culture by paying attention to chemicals like this. Some countries demand regular training and reporting on even minor toxicants. Open databases and accessible data mean fewer questions about what’s hazardous and more time spent on solutions. It never hurts to ask for a material safety data sheet—even if you end up learning that you already have excellent habits.
A Look at Methyl 2-Bromooctanoate Purity
Methyl 2-Bromooctanoate lands on the ordering list of chemical labs and manufacturing plants for good reason. It's not just another intermediate; this compound acts as a reliable building block for synthesizing pharmaceuticals and specialty chemicals. Purity always jumps off the page in any product specification, but it carries even more weight for a niche reagent like this one. In real-world purchasing, the offered purity almost always reads “≥98%.” You’ll see suppliers promising anywhere from 98% up to 99%, sometimes verified by gas chromatography. Anything below that starts to prompt questions from picky chemists and quality control teams.
Why Purity Makes the Difference
Contaminants cause headaches. Even a sliver of impurity in a batch of Methyl 2-Bromooctanoate can set off a chain reaction — literally, in synthetic chemistry. In a pharmaceutical context, that means failed reactions, reduced yields, or extra steps at the purification bench. Nobody wants to run extra columns or spot mysterious ghosts in NMR spectra. When I worked in a lab in grad school, I saw first-hand how an “almost pure” reagent held back a synthesis. Time lost. Money wasted. Purity isn’t just a detail; it’s the line between a one-day job and a one-week grind.
How Labs Assess Quality
Quality-minded chemists run a few tests the moment a bottle lands on their bench. Gas chromatography and NMR become the go-to tools for this compound. If you see a specification sheet, you’ll usually notice a line stating: “Purity: ≥98% (GC).” Any major supplier who values its reputation puts real effort into corroborating that number. Impurities, such as unreacted acids, related esters, or residual solvents, show up with sensitive analytical techniques. A reputable supplier will flag these and guarantee they stay below 2%.
Who Sets the Standard?
Big chemical companies don’t make up these numbers out of thin air. The industry sets unofficial benchmarks through years of back-and-forth with researchers and manufacturers. Universities, pharmaceutical developers, and process chemists give feedback after every order. If batches don’t meet the 98% mark, complaints start to pile up, and that supplier gets nudged off the preferred list. There’s healthy pressure to keep the minimum bar high, especially for substances handy for further derivatization.
Risks of Lower Purity and Solutions
Cut-rate batches might cost a bit less upfront, but anyone using them for sensitive synthesis can end up paying much more in labor and materials. Sometimes labs try to fix a low-purity sample with homemade purification, but that usually eats up valuable time. A far better approach involves pushing for transparency from suppliers: audit certificates of analysis, demand analytical data, and keep records. Outsourcing purification or switching to a trusted vendor can sidestep a lot of stress down the road.
Keeping the Quality High
Supplier selection, solid specifications, and regular incoming testing close the loop. Buyers who stick to ≥98% purity standards find fewer problems scaling up. Sharing feedback with vendors helps everyone in the chain. From a practical viewpoint, the extra effort spent checking and confirming quality pays off every time a smooth reaction — and a cleaner notebook — follows.