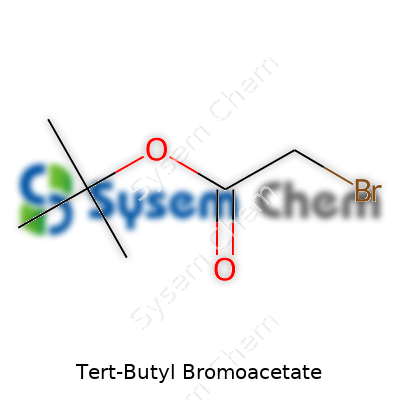
Tert-Butyl Bromoacetate: Research, Application, and Impact
Historical Development
The name tert-butyl bromoacetate means a lot in any chemistry lab committed to pushing the boundaries of synthesis. Since the early surge in organic chemistry, the search for reliable alkylating agents carved a place for bromoacetates on lab shelves. This particular ester slowly found favor as chemists realized its stability in storage and convenience for alkylation or protecting group strategies. Over decades, improvements in industrial synthesis reduced impurities and lowered cost. Back at university, discussions often included the challenge of selecting protecting groups in multistep synthesis. Tert-butyl bromoacetate rose in these stories due to its ease of installation and clean removal, especially in peptide and small-molecule projects. Anyone who’s faced the annoyance of side reactions from unstable esters or hazardous halides appreciates why bromoacetates stuck around. The molecule’s climb from research curiosity to catalog staple shows how stepwise organic chemistry shapes the chemical manufacturing world.
Product Overview
This compound, best described by its functional groups—a tert-butyl ester linked to a bromoacetate backbone—works in diverse synthesis pathways. Labs rely on it for introducing tert-butoxycarbonyl-protected acetic acid units. While it's clear that chemicals serve different needs, tert-butyl bromoacetate draws attention for how it enables selective reactivity. Its clear, colorless liquid form pours readily and blends without clogging pipettes, keeping bench work smooth. Familiar catalog numbers and the acrid but manageable scent mark its spot among reagents ready for action, never buried too far from reach. Researchers keep this bottle close when strategizing SN2 reactions or constructing complex heterocycles.
Physical & Chemical Properties
You’ll find tert-butyl bromoacetate’s boiling point around 147-149°C at atmospheric pressure, with density sitting near 1.32 g/cm³ at 25°C. The refractive index measures close to 1.438-1.441, reflecting its purity and consistency batch-to-batch. The liquid’s low viscosity helps in measuring and mixing. It dissolves well in ether, chloroform, and most polar aprotic solvents, retaining some moisture sensitivity—humidity never does any favors here. A sweet, faintly spicy odor lingers but doesn’t overwhelm. Bromoacetates react vigorously with nucleophiles, as the bromo group works as a classic leaving group, giving this molecule a slot in the chemist’s essential toolkit.
Technical Specifications & Labeling
Catalog entries for tert-butyl bromoacetate usually stipulate a purity of 98% or higher, vital for avoiding troublesome byproducts. Bottle labels display molecular formula C6H11BrO2, molecular weight 195.06 g/mol, standard storage instructions—usually cool, dry, sealed from air—and hazard statements per global harmonized standards. Labels also warn about possible severe skin or eye irritation and respiratory effects, supported by GHS pictograms and hazard codes (such as H314 or H315). The clear, detailed technical data sheets provided by reputable vendors detail NMR and GC-MS verification methods, batch numbers for traceability, and application notes in English, German, or Chinese.
Preparation Method
Chemists often prefer synthesizing tert-butyl bromoacetate using an SN2 approach: bromoacetyl bromide reacting with tert-butyl alcohol in the presence of a base like pyridine or triethylamine. The reaction produces the desired ester while capturing acidic byproducts in situ. From my experience, keeping the temperature steady and ensuring a dry atmosphere reduces hydrolysis and maximizes yield. The need for careful separation—usually column chromatography or vacuum distillation—can’t be overstated for those chasing high-purity product. In some industrial plants, continuous flow reactors have replaced batch techniques, yielding more consistent material at scale.
Chemical Reactions & Modifications
Tert-butyl bromoacetate’s role as an alkylating agent makes it a star in C–C and C–N bond construction. It reacts smoothly with primary or secondary amines, producing tert-butyl N-alkyl bromoacetates. Chemists lean on this molecule for easy access to carboxylic acid derivatives: after its incorporation, a simple acid-catalyzed deprotection liberates acetic acid. Its reactivity also extends to Grignard or organolithium reagents, where the tert-butyl ester slows unwanted side reactions. The bromo group invites nucleophilic substitutions—think thiols or alkoxides—expanding the toolbox for medicinal chemistry or agrochemical discovery. Its predictable breakdown under mild acids offers a clean “switch,” turning a protected intermediate into a free acid with a single step.
Synonyms & Product Names
Catalogs and journals use several names: tert-butyl bromoacetate, bromoacetic acid tert-butyl ester, TBBA, and 2-bromoacetic acid tert-butyl ester. European suppliers lean on EINECS numbers or CAS No. 5292-43-3 for ordering. Synonyms can trip up new researchers who overlook close matches in databases, yet old hands in procurement always scan for both IUPAC and common product codes to avoid confusion.
Safety & Operational Standards
Safety matters. MSDS documentation stresses strict glove and mask use, strong ventilation, and immediate cleanup of spills, given its potential for eye, skin, and respiratory irritancy. No one in the lab wants careless chemical burns or lingering coughs, so eye wash stations turn into mandatory stops, not afterthoughts. Fume hoods stay down, and waste flows into halogenated collection streams for regulatory compliance. Those working with larger batches move through hazmat drills and buddy checks, since larger spills or inhalation risks become real. Training new team members in safe reagent handling means repeating steps, checking gloves, and taping flasks—a habit worth the minutes it takes.
Application Area
Pharmaceutical companies covet tert-butyl bromoacetate as a precursor for active molecule assembly, often in kinase inhibitor or amino acid derivative synthesis. In the biotech startup world, scale-up chemists eyed this compound for high-purity peptide fragment production, benefiting from easy selective group activation and later removal. Fine chemical makers favor it for certain herbicides or insecticides, where its clean breakdown means less impact after application. Analytical chemists, meanwhile, turn to it for preparing calibration or derivatization standards in LC-MS workflows. Some high-end electronics research labs use ter-butyl bromoacetate as a building block for customized surface modification of sensor platforms. Literature points to growing roles in library synthesis, combinatorial techniques, and even odorant molecule prep in flavor-and-fragrance R&D.
Research & Development
R&D teams appreciate tert-butyl bromoacetate as a platform for testing new coupling or alkylation methods, and as a benchmark for evaluating alternative protecting groups. Researchers trying to cut out hazardous intermediates often look for safer substitutes but keep returning to bromoacetates due to their reliability. Projects exploring greener synthesis techniques focus on solvent management and minimizing brominated byproduct generation. At conferences, poster sessions often showcase tweaks in reagent concentration or temperature, aiming for cleaner reactions and fewer purification headaches. Collaborations between universities and industry sometimes hinge on the availability of high-quality tert-butyl bromoacetate, underlining its role as a quiet enabler of modern synthetic work.
Toxicity Research
Toxicologists keep a close watch on compounds bearing both ester and bromo groups. Tert-butyl bromoacetate doesn’t escape scrutiny; animal studies note moderate acute toxicity, with irritation reported in eye and skin models. The bromoacetate backbone can disrupt cellular metabolic pathways in sufficiently high doses, though actual occupational exposure levels seldom approach these extremes. Chronic exposure data remain sparse, with regulatory bodies still urging conservative handling practices. Researchers active in environmental science examine breakdown rates and metabolite profiles, tracking potential persistence in soil or water. Safety reviews stress avoiding inhalation, direct skin contact, or ingestion, and maintaining quick access to emergency protocols.
Future Prospects
As green chemistry trends reshape industrial practice, efforts to produce tert-butyl bromoacetate with reduced environmental footprint are on the rise. Teams investigate more sustainable bromination methods, solvent recycling, and improved extraction protocols to curb waste. Companies want biodegradable protecting groups—chemically robust but easy to break down after use. Some startups tinker with enzymatic or electrochemical techniques, aiming for selectivity without hazardous reagents. Regulators and corporate labs alike pay attention to improved labeling, packaging using recycled plastics, and documentation that tracks every gram from source to shelf. The compound remains a staple, but as synthesis techniques and safety standards evolve, so do expectations for cleaner, smarter, and safer processes anchored by robust science and transparent data sharing.
From Labs to Life: The Chemical’s Role
Tert-Butyl Bromoacetate doesn’t catch the spotlight like aspirin or baking soda, but in any synthetic chemistry lab, it gets noticed for what it brings to the table. I’ve seen organic chemists reach for this compound as a staple building block, especially while piecing together molecules that might one day turn into treatments or specialty materials.
Chemistry That Matters
The secret sauce with tert-butyl bromoacetate lies in its two features attached to a single carbon: a tert-butyl ester (which shields acids until needed) and a bromine atom (which makes reactions with other chemicals easier). For chemists pushing boundaries in drug discovery or developing dyes, this compound acts as a bridge. I remember colleagues in graduate school leaning on its predictable behavior—the way its bromine swaps places so cleanly with other chemical groups kept experiments running smoothly, which saves hours and resources when trial and error aren’t a luxury.
Pharmaceuticals and Beyond
The pursuit for new medicines often starts with a small molecule that can be tweaked again and again. Tert-butyl bromoacetate steps in during these early steps, letting researchers assemble complicated structures by adding carbon chains piece by piece. Real progress comes from having reliable tools. This compound’s stability means reactions get consistent results, so there is less uncertainty about what’s bubbling up in the flask. In my work with researchers, I’ve seen how a single step in a ten-stage synthesis can make or break a year’s worth of effort. Tert-butyl bromoacetate often ends up featured in the early diagrams for drugs aimed at diseases like cancer or viral infections.
Specialty Chemicals and Industry Impact
It isn’t just the pharmaceutical world that taps into this chemistry. Companies crafting flavors, fragrances, and agricultural additives rely on tert-butyl bromoacetate’s knack for making new bonds. The reason is simple: it’s easier to experiment with new ingredients if you have reliable reagents. I once toured a pilot plant where kilo batches of intermediates were being prepared. Using tert-butyl bromoacetate kept the process safer and the yield higher, since it reacts without causing side-products that gunk up the process—something that matters when every impurity can lead to wasted money or failed regulatory tests.
Challenges and Responsible Handling
No tool comes without issues. Tert-butyl bromoacetate is toxic, and more than one safety sheet warns: gloves and fume hoods are non-negotiable. I’ve witnessed the effects of lax enforcement—skin burns and headaches surface quickly if protocols get ignored. Environmental stakes are real too. As regulations increase, waste management practices in companies using chemicals like this matter more. I’ve seen research teams innovate around greener alternatives or minimize waste, but until replacements catch up, training and strict oversight remain the most practical response.
What’s Next
As industries strive for cleaner and safer chemistry, the story of tert-butyl bromoacetate keeps changing. Its value in making tomorrow’s medicines and materials is real, but the search continues for safer, more sustainable chemistry. Each improvement in safer design and handling not only protects workers but builds confidence in the products we all rely on.
Understanding the Structure
Tert-butyl bromoacetate goes by the chemical formula C6H11BrO2. In some labs, it answers to its name with a calm, colorless liquid appearance. I remember running across it early in my research career, confused at first by the mix of letters and numbers. Nothing about the name screams everyday use, but its structure packs a punch in chemistry circles. The core of this compound holds a tert-butyl group attached to an ester body, with a bromoacetate piece offering unique reactivity.
Real Work in Organic Synthesis
In practical organic chemistry, this molecule plays its part as a handy building block. I’ve seen grad students reach for tert-butyl bromoacetate when they’re piecing together amino acids or designing custom esters. It works because the bromo group can easily swap out with other units, letting chemists build much larger, more complex molecules. These reactions don’t just happen in textbooks; they power up everything from drug creation to new materials.
That reactivity comes from its formula and body. The tert-butyl end protects other parts of a molecule, which solves a lot of headaches during multi-step synthesis. You can dodge side-reactions and peel off the protection right at the finish line. This saves time and cuts down on waste, which matters for tight research budgets and deadlines.
Health and Safety Concerns
Though a solid workhorse, bromoacetate compounds can spark real safety concerns if not handled with respect. I remember the sharp, prickly odor from an open vial, kind of like a warning sign. Breathing in too much, or getting some on the skin, can cause harsh reactions. In my experience, good habits like gloves, lab coats, and working in a fume hood are more than just rules—they keep people healthy and research moving.
Accidental spills grow risky fast. Tert-butyl bromoacetate contains a bromine atom, and that makes it more reactive and toxic than simpler esters. I saw a case where a bottle slipped from the benchtop and broke. Quick response with absorbent pads, followed by waste collection in a sealed bag, protected everyone in the room. Stories like that stick with you and remind us how important it is to stay alert in the lab.
Problems and Solutions in Storage and Disposal
One overlooked problem involves storage. Light and air can break down the compound and make it even more unpredictable. I’ve always kept bottles tightly sealed, away from heat and sunlight, on a lower shelf meant for hazardous reagents. Proper labeling gives every researcher a heads-up if they reach for the wrong bottle in a hurry.
Disposal can turn tricky too. Pouring leftover material down a sink isn’t an option. The right call involves using official hazardous waste programs provided by institutions. Trained staff take it from there, sending it off for safe destruction rather than risking harm to waterways or communities.
Building Better Practices
We rely on tert-butyl bromoacetate for its smart, reliable chemistry. I’ve seen well-run labs develop detailed handling procedures and share safety stories during group meetings. That helps everybody, from new interns to experienced postdocs, keep mistakes rare. The right balance involves respect for every chemical and a willingness to adapt when things change.
The Real Risks Behind Poor Storage
Tert-butyl bromoacetate doesn’t get as much attention outside chemistry circles, but anyone who has dealt with lab chemicals knows how important storage conditions become for both safety and product quality. You handle this liquid with respect because it reacts with water, standing ready to release bromoacetic acid and tert-butyl alcohol. Even a little moisture creeping into the bottle causes problems you might not spot until the experiment gives odd results.
Ask people who’ve worked with old samples: sometimes the whole bottle contents turn yellow or give off a smell nobody wants in a shared workspace. The hydrolysis you can get if water joins the mix isn’t pretty or predictable. Those experiences underline why correct storage isn’t bureaucratic red tape—it’s professional self-defense, not only for results but for health.
Keeping It Cool, Dry, and Dark
Tert-butyl bromoacetate stays most stable in a visibly dry area, well away from sunlight. Ultraviolet light can trigger breakdowns in many organic compounds, and with bromoacetates you risk both product loss and new, unwanted byproducts. I’ve watched plastic bottles begin to warp or sweat just from improper shelf placement—leaving things next to sunny windows out of habit or in spaces where temperature fluctuates every day. Items kept in climate-controlled cabinets or fridges stay more consistent.
Don’t even consider common household refrigerators. Cross-contamination with food or drink would be a nightmare—and temperature swings caused by frequent door openings can turn a stable chemical into a risky mess. Labs equipped with dedicated chemical refrigeration keep substances below 8°C, mainly to slow down both evaporation and chemical degradation. Consistent cold means less chance for the liquid to develop hazardous fumes or break down into anything unpredictable.
The Air We Breathe… and Don’t Want in the Bottle
Humidity indoors changes a lot by season and by city, but in any lab, low moisture levels matter. Desiccators—either the classic vacuum-sealed jars or cabinets lined with silica gel—create an environment that sharply reduces risk of moisture wrecking reactive chemicals. I’ve seen plenty of bottles kept on high, dusty open shelves "for convenience," but quick access rarely makes up for ruined product or accidental exposure due to spillage. Always check the bottle seal before use.
Ventilation matters just as much as moisture control, though. Fume hoods aren’t only for mixing or pouring, but also for opening bottles of volatile or toxic reagents. Even brief exposure can lead to irritation or cough, particularly in crowded teaching labs. It’s not worth cutting corners, especially for new chemists who may not notice a faint odor until it’s too strong to ignore.
Labeling, Segregation, and Responsibility
Another real-world challenge involves making sure every bottle tells the truth—about date received, date opened, and hazard class. If you ever watched someone guessing an unlabeled bottle, you can imagine the anxiety from not knowing whether it’s flammable, corrosive, or toxic. Tert-butyl bromoacetate sits solidly in the "handle with care" category, so it belongs away from acids, bases, and especially from strong reducing agents or oxidizers.
Good storage practices don’t only save money or time. They provide accountability and protect people. The best labs set up monthly checks; someone looks at all bottles for changes in color, seal integrity, and expiration dates, instead of waiting for an inspection to catch problems. This culture of shared vigilance keeps risk low and trust high.
Steps Forward: Training and Design
Training new lab members on why each step matters shifts storage habits for the better. Add clear signage, set up storage maps, and use regular drills—those efforts build muscle memory and keep incidents rare. Chemical supply companies should make storage guidelines part of every delivery, not just small print on the data sheet buried in packaging. At the end of the day, active attention to detail—not fancy storage units—makes the biggest difference.
Understanding What You’re Working With
Tert-Butyl Bromoacetate is one of those chemicals that looks fine in a bottle but turns into a real problem if you ignore basic laboratory safety. It sits on many lab shelves because it's useful in organic synthesis. After spending years working in research labs, I've seen both good habits and close calls. Tert-Butyl Bromoacetate can cause burns, intense eye irritation, and may trigger respiratory issues. Its toxic profile also gives no second chances—one quick splash or a sniff too close can lead to painful consequences.
Personal Protective Equipment: The Non-Negotiables
A set of gloves may sound obvious, yet I've watched experienced chemists reach for nitrile gloves only to ignore the importance of eye protection. Always use goggles with a snug fit, not just basic safety glasses. Lab coats with cuffs help, especially when you remember that splashes bounce.
A simple mask won’t cut it—go for a well-fitted respirator if there’s any risk of aerosol or vapor. Skin contact is dangerous, so any exposed area weakens your defense. Closed-toe shoes are a must; chemical spills on open-toed sandals are more common than you'd think.
Working Environment: The Fume Hood Fable
Saving a few minutes outside the fume hood often seems harmless. In reality, fumes build up fast and spread. Keep all work with Tert-Butyl Bromoacetate inside a functioning, well-maintained hood. Check that the sash height sits at a safe level. I once saw a colleague suffer a serious cough because ventilation wasn’t checked before starting the reaction.
Your workspace tells you a lot about your risk. Keep unnecessary chemicals far from your reaction setup. Clear benches lower the odds of cross-contamination or accidental spills.
Storage Smarts and Spills
Store this chemical in a tightly sealed container and away from heat. Small variations in storage temperature can increase pressure, risking leaks. Always use compatible storage bottles—polyethylene or glass works well, but old, scratched containers don’t.
Spills need immediate attention. Baking soda isn’t a magic solution for every spill, but for small Tert-Butyl Bromoacetate spills, sand or a chemical absorbent beats a frantic scramble. Never use paper towels—they don’t contain the chemical, they just spread it.
Training and Teamwork
Written protocols exist for a reason. Skipping the safety data sheet risks more than a reprimand. Even if you’ve handled similar chemicals, every batch and supplier brings different risk. In a group setting, keep everyone informed. If you see someone skip a step, say something—calling out someone’s oversight early on prevents accidents. And after an incident, share the story. Labs that talk openly about near-misses have fewer serious accidents in the long run.
Emergency Planning
Accidents still happen. An eyewash station and safety shower lose their value if you can’t reach them blindfolded—practice the path. Know the emergency contacts and spill response procedures without needing to check a binder in the heat of the moment. Follow up every exposure with medical attention, even if you think it’s no big deal. Shortcuts often lead to regret when it comes to chemical safety.
Understanding What You're Really Getting
As someone who’s navigated a fair share of chemistry labs and ordered specialty chemicals for a wide range of projects, I see the same question asked again and again. What exactly does “purity grade” mean when we buy something like Tert-Butyl Bromoacetate? For a novice, it sounds simple: high purity must be better. But for the rest of us, who’ve dealt with uncooperative reactions and unexplained failures, purity means much more than a single percentage on the label.
Purity Isn’t Just a Number
Most bottles show numbers like 97%, 98%, or 99%. Traces of water, residual solvents, or leftover reagents don’t show up until you have trouble reproducing results. A synthesis that should yield a clean intermediate ends up speckled or discolored. Worse, downstream steps start to drag—byproducts, splits in NMR peaks, impurities riding along into the final workup. These small things snowball, especially for scale-ups where extra impurities turn minor annoyances into outright project risks.
Research-grade Tert-Butyl Bromoacetate often claims a minimum 98% purity. What suppliers don’t always highlight: what makes up the elusive remainder. I’ve opened vials where even trace halides or pH fluctuations have changed outcomes. Maybe the spec sheet gives you faint gas chromatography lines, left unlabeled, or sets water content as “loss on drying,” which doesn’t mean zero.
Why It Matters to the Workbench
Years of troubleshooting have taught me that high-purity reagents save time and money. Take the difference between two batches sharing the same purity on paper. One batch feels oily, carries a faint pungent smell, clings to the glass. The other crystallizes clean. Analytical data provide clues, but end-use matters more. A pharmaceutical synthesis, for instance, faces real regulatory hurdles: every microgram of impurity counts, every unknown complicates submissions and surprise audits. Fine chemicals for materials science might tolerate a slightly broader envelope, but who wants batch-to-batch headaches and time wasted on purification?
A supplier might advertise “analytical” grade, “reagent” grade, or even “custom-spec” products. I’ve found asking directly for HPLC, NMR profiles, or impurity reports tells the real story—sometimes even catching errors before a project derails. Trust in a vendor starts with full transparency, not just a glossy certificate of analysis. Cross-checks with independent analysis, or going through a reputable supplier, can pay dividends in long-term project reliability.
Practical Steps Before Ordering
If you’re in a field where the purity of Tert-Butyl Bromoacetate makes or breaks your results—drug discovery, agrochemistry, fine materials—don’t accept certificates at face value. Always request recent data: batch chromatograms, NMR spectra, and any specific impurity cutoffs. Look beyond “typical” values, especially if your project moves from milligrams to multi-gram scale. In my own practice, I’ve always favored suppliers who offer customization—who willingly provide details on manufacturing origin, lot traceability, and who are prepared to discuss failed quality checks openly.
Ultimately, asking the right questions up front protects your time, budget, and reputation. Sure, a higher purity costs more, but it often pays off in longer shelf life, repeatable yields, and fewer late-night troubleshooting sessions. Consistency and trust matter far more than a simple purity percentage on a label.